THE BIBLICAL STORY
The Holy Scriptures tell us that when our Lord was dying on the Cross, He saw His mother and His disciple John and said to the Virgin Mary, "Woman, behold your son!" and to John, "Behold your mother!" (John 19:25-27). From that hour, the Apostle took care of the Theotokos in his own home.
Along with the biblical reference in Acts 1:14 that confirms that the Virgin Mary was with the Holy Apostles on the day of Pentecost, the tradition of the Church holds that she remained in the home of the Apostle John in Jerusalem, continuing a ministry in word and deed.
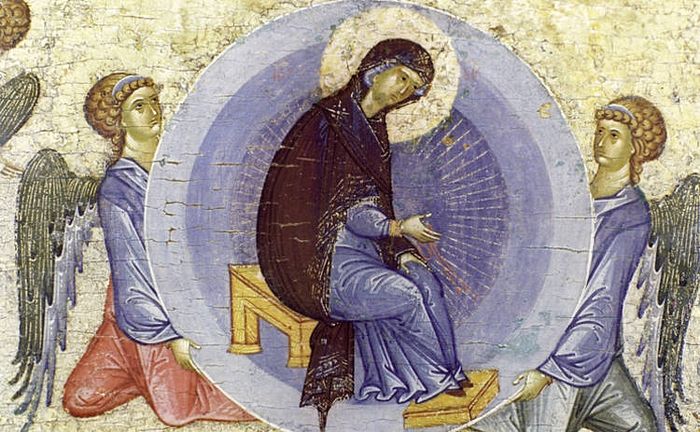
At the time of her death, the disciples of our Lord who were preaching throughout the world returned to Jerusalem to see the Theotokos. Except for the Apostle Thomas, all of them including the Apostle Paul were gathered together at her bedside. At the moment of her death, Jesus Christ himself descended and carried her soul into heaven.
Following her repose, the body of the Theotokos was taken in procession and laid in a tomb near the Garden of Gethsemane. When the Apostle Thomas arrived three days after her repose and desired to see her body, the tomb was found to be empty. The bodily assumption of the Theotokos was confirmed by the message of an angel and by her appearance to the Apostles.
CELEBRATION OF THE FEAST OF THE DORMITION
The commemoration of the Dormition of the Theotokos and the preparation for the Feast begin on August 1 with a period of fasting. A strict fast is followed on most of the days (no meat, dairy, oil, or wine), with the exceptions of fish on the Feast of the Transfiguration (August 6) and the day of the Dormition. Oil and Wine are allowed on Saturdays and Sundays.
The Church Year
Dormition of the Theotokos
The feast of the Dormition or Falling-asleep of the Theotokos is celebrated on the fifteenth of August, preceded by a two-week fast. This feast, which is also sometimes called the Assumption, commemorates the death, resurrection and glorification of Christ’s mother. It proclaims that Mary has been “assumed” by God into the heavenly kingdom of Christ in the fullness of her spiritual and bodily existence.
As with the nativity of the Virgin and the feast of her entrance to the temple, there are no biblical or historical sources for this feast. The Tradition of the Church is that Mary died as all people die, not “voluntarily” as her Son, but by the necessity of her mortal human nature which is indivisibly bound up with the corruption of this world.
The Byzantine Church teaches that Mary is without personal sins. In the Gospel of the feast, however, in the liturgical services and in the Dormition icon, the Church proclaims as well that Mary truly needed to be saved by Christ as all human persons are saved from the trials, sufferings and death of this world; and that having truly died, she was raised up by her Son as the Mother of Life and participates already in the eternal life of paradise which is prepared and promised to all who “hear the word of God and keep it.” (Luke 11:27-28)
In giving birth, you preserved your virginity. In failing asleep you did not forsake the world, O Theotokos. You were translated to life, O Mother of Life, and by your prayers, you deliver our souls from death. (Troparion)
Neither the tomb, nor death, could hold the Theotokos, who is constant in prayer and our firm hope in her intercessions. For being the Mother of Life, she was translated to life, by the One who dwelt in her virginal womb. (Kontakion)
The services of the feast repeat the main theme, that the Mother of Life has “passed over into the heavenly joy, into the divine gladness and unending delight” of the Kingdom of her Son. (Vesper verse) The Old Testament readings, as well as the gospel readings for the Vigil and the Divine Liturgy, are exactly the same as those for the feast of the Virgin’s nativity and her entrance into the Temple. Thus, at the Vigil we again hear Mary say: “My soul magnifies the Lord and my Spirit rejoices in God my Saviour.” (Luke 1:47) At the Divine Liturgy we hear the letter to the Philippians where St. Paul speaks of the self-emptying of Christ who condescends to human servitude and ignoble death in order to be “highly exalted” by God his Father. (Philippians 2:5- 11) And once again we hear in the Gospel that Mary’s blessedness belongs to all who “hear the word of God and keep it.” (Luke 11:27-28)
Thus, the feast of the Dormition of the Theotokos is the celebration of the fact that all men are “highly exalted” in the blessedness of the victorious Christ, and that this high exaltation has already been accomplished in Mary the Theotokos. The feast of the Dormition is the sign, the guarantee, and the celebration that Mary’s fate is, the destiny of all those of “low estate” whose souls magnify the Lord, whose spirits rejoice in God the Saviour, whose lives are totally dedicated to hearing and keeping the Word of God which is given to men in Mary’s child, the Saviour and Redeemer of the world.
Finally it must be stressed that, in all of the feasts of the Virgin Mother of God in the Church, Byzantine Christians celebrate facts of their own lives in Christ and the Holy Spirit. What happens to Mary happens to all who imitate her holy life of humility, obedience, and love. With her all people will be “blessed” to be “more honorable than the cherubim and beyond compare more glorious than the seraphim” if they follow her example. All will have Christ born in them by the Holy Spirit. All will become temples of the living God. All will share in the eternal life of His Kingdom who live the life that Mary lived.
In this sense everything that is praised and glorified in Mary is a sign of what is offered to all persons in the life of the Church. It is for this reason that Mary, with the divine child Jesus within her, is call in the Byzantine Tradition the Image of the Church. For the assembly of the saved is those in whom Christ dwells.
It is the custom in some churches to bless flowers on the feast of the Dormition of the Holy Theotokos.
From: The Orthodox Faith: Volume II Worship